Effects of eicosapentaenoic acids on oxidative stress and plasma fatty acid composition in patients with lupus nephritis.
Norio Nakamura, Ryuichiro Kumasaka, Hiroshi Osawa, Hideaki Yamabe, Ken-Ichi Shirato, Takeshi Fujita, Rei-Ichi Murakami, Michiko Shimada, Masayuki Nakamura, Ken Okumura, Kei Hamazaki, Tomohito Hamazaki
文献索引:In Vivo 19(5) , 879-82, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is one of the major components of fish oil, which was reported to have antiatherogenic, anti-inflammatory and immune suppressive effects. In the present study, highly purified EPA was administered to patients with lupus nephritis and the effects of EPA on urinary 8-isoprostane, a reliable marker of oxidative stress, were investigated in these patients. Six outpatients (1 man and 5 women), with lupus nephritis diagnosed by renal biopsy, were entered in the study. We administered 1800 mg EPA ethyl-ester (purity > 95%) daily and examined the urinary 8-isoprostane levels and plasma fatty acid composition before and 3 months after EPA treatment. The urinary 8-isoprostane levels were significantly decreased after the treatment compared with those before the treatment (from 530 +/- 113 pg/mg x Cr to 235 +/- 49 pg/mg x Cr, p = 0.02). The EPA levels in the plasma phospholipid (PL) fraction were significantly increased after the treatment (from 3.30 +/- 0.64 mol% to 8.01 +/- 0.47 mol%, p < 0.001). Arachidonic acid (AA) levels in the plasma PL fraction were significantly decreased after the treatment (from 9.47 +/- 0.28 mol% to 7.33 +/- 0.43 mol%, p < 0.001). The ratios of EPA to AA were significantly increased after the treatment (from 0.35 +/- 0.07 to 1.14 +/- 0.16, p < 0.001). Thus, this preliminary study indicated that EPA might exert beneficial effects on lupus nephritis by decreasing the oxidative stress.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
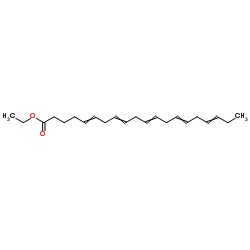 |
EPA乙酯
CAS:73310-10-8 |
C22H34O2 |
|
Protective effects of prescription n-3 fatty acids against i...
2011-07-01 [Food Funct. 2(7) , 386-94, (2011)] |
|
Usefulness of colon targeted DHA and EPA as novel diabetes m...
2008-12-08 [J. Control. Release 132(2) , 99-104, (2008)] |
|
Identification of inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediat...
2008-06-01 [Am. J. Hematol. 83(6) , 437-45, (2008)] |
|
Highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid prevents the progressi...
2009-04-01 [Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 80(4) , 229-38, (2009)] |
|
Does eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) inhibit cerebral vasospasm ...
2008-07-01 [Acta Neurol. Scand 118(1) , 54-9, (2008)] |