Microbial degradation of chlorinated acetophenones.
J Havel, W Reineke
文献索引:Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59(8) , 2706-12, (1993)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A defined mixed culture, consisting of an Arthrobacter sp. and a Micrococcus sp. and able to grow with 4-chloroacetophenone as a sole source of carbon and energy, was isolated. 4-Chlorophenyl acetate, 4-chlorophenol, and 4-chlorocatechol were identified as metabolites through comparison of retention times and UV spectra with those of standard substances. The proposed pathway was further confirmed by investigation of enzymes. The roles of the two collaborating strains were studied by growth experiments and on the level of enzymes. If transient accumulation of 4-chlorophenol was avoided either by the use of phenol-absorbing substances or by careful supplement of 4-chloroacetophenone, the Arthrobacter sp. was able to grow as a pure culture with 4-chloroacetophenone as a sole source of carbon and energy. Several mono-, di-, and trichlorinated acetophenones were mineralized by the Arthrobacter sp.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
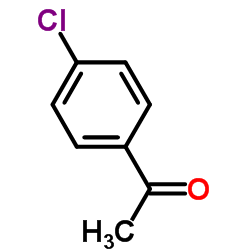 |
对氯苯乙酮
CAS:99-91-2 |
C8H7ClO |
|
Screening of microorganisms producing cold-active oxidoreduc...
2011-01-01 [Mar. Drugs 9 , 889-905, (2011)] |
|
Thienylhalomethylketones: Irreversible glycogen synthase kin...
2009-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 6914-25, (2009)] |
|
Optimization of culture conditions to produce high yields of...
2011-01-01 [BMC Biotechnol. 11 , 110, (2011)] |
|
[Morphological findings in the rabbit cornea after tear gas ...
1982-01-01 [Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 218(4) , 177-84, (1982)] |