The nicotinic α7 receptor agonist GTS-21 improves cognitive performance in ketamine impaired rhesus monkeys.
Christopher E Cannon, Vanita Puri, Jeffrey A Vivian, Melissa S Egbertson, Donnie Eddins, Jason M Uslaner
文献索引:Neuropharmacology 64 , 191-6, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia are recognized as a core component of the disorder, yet there remain no available therapeutics to treat these symptoms of the disease. As a result, there is a need for establishing predictive preclinical models to identify the therapeutic potential of novel compounds. In the present study, rhesus monkeys were trained in the object retrieval-detour task, which is dependent on the prefrontal cortex, a brain region implicated in the cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia. The NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine significantly impaired performance without affecting measures of motor or visuospatial abilities. Pre-treatment with the nicotinic α7 agonist GTS-21 (0.03 mg/kg) significantly attenuated the ketamine-induced impairment, consistent with reports from clinical trials suggesting that nicotinic α7 receptor agonism has pro-cognitive potential in clinical populations. In contrast, pretreatment with the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor donepezil failed to reverse the ketamine-induced impairment, consistent with studies showing a lack of pro-cognitive effects in patients with schizophrenia. These data suggest that the ketamine-impaired object retrieval-detour task could provide a model with improved predictive validity for drug development, and confirm the need for additional efforts in back-translation. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled 'Cognitive Enhancers'.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
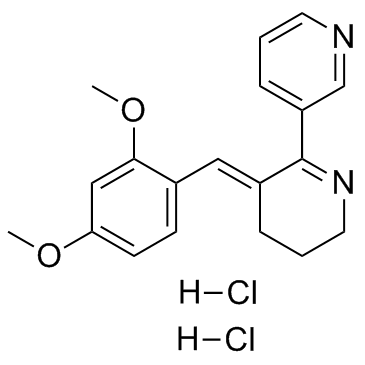 |
GTS-21二盐酸盐(DMBX-A)
CAS:156223-05-1 |
C19H22Cl2N2O2 |
|
Central muscarinic cholinergic activation alters interaction...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(10) , e109272, (2014)] |
|
Pro-cognitive activity in rats of 3-furan-2-yl-N-p-tolyl-acr...
2015-11-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 , 5123-35, (2015)] |
|
The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands methyllycaco...
2012-10-15 [J. Neuroimmunol. 251(1-2) , 65-72, (2012)] |
|
Functional magnetic resonance imaging of effects of a nicoti...
[Biol. Psychiatry 35(4) , 938-42, (2010)] |
|
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists attenuate septic a...
2012-01-01 [PLoS ONE 7(5) , e35361, (2012)] |