Assessment of triethanolamine salicylate release from the dermatological bases and the commercial products.
A Babar, P J Chickhale, F M Plakogiannis
文献索引:Pharm. Acta Helv. 66(12) , 322-8, (1991)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Recently, triethanolamine salicylate (TEAS) is frequently being incorporated in several over-the-counter topical analgesic pharmaceutical products. Since the clinical efficacy of such dosage form depends upon the release of the active ingredient at the site of application, the present study was undertaken to study the in vitro release of the (TEAS) from commonly used ointment bases and two most popular commercial products in the U.S. market. Also, the effects of various penetration enhancers, such as, ethanol, propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol-400, dimethyl-sulfoxide (DMSO), polysorbate-80 and urea were evaluated. In general, the drug release from the experimental formulations was higher than the commercial products studied. The inclusion of the penetration enhancing ingredients increased the drug release from some of the formulations evaluated. The hydrophilic emulsion base with 10% ethanol exhibited the best in vitro drug release. The apparent viscosity profiles of the formulations showed no definite relationship with the amounts of drug release. However, significant differences in the (TEAS) release from the experimental formulations were observed.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
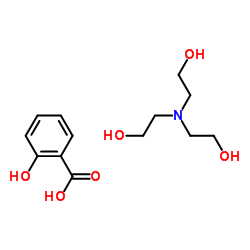 |
三乙醇胺水杨酸盐
CAS:2174-16-5 |
C13H21NO6 |
|
Topical penetration of commercial salicylate esters and salt...
1998-07-01 [Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 46(1) , 29-35, (1998)] |
|
Serum concentrations of salicylic acid following topically a...
1996-09-01 [Ann. Pharmacother. 30(9) , 935-40, (1996)] |
|
Self promotion of deep tissue penetration and distribution o...
1999-03-01 [Pharm. Res. 16(3) , 427-33, (1999)] |
|
Trolamine salicylate cream in osteoarthritis.
1982-10-01 [JAMA 248(13) , 1577-8, (1982)] |
|
Comparison of topical anti-ischemic agents in the salvage of...
1999-01-01 [Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 1(1) , 27-32, (1999)] |