Methionine-induced phytoalexin production in rice leaves.
Y Nakazato, S Tamogami, H Kawai, M Hasegawa, O Kodama
文献索引:Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64(3) , 577-83, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The application of methionine on wounded rice leaves induced the production of rice phytoalexins, sakuranetin and momilactone A. This induction resulted from stimulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase activity. Jasmonic acid, ethylene, and active oxygen species are important as signal transducers in disease resistance mechanisms. However, although the endogenous level of jasmonic acid rapidly increased in reaction to wound, methionine treatment could not induced endogenous JA production. Ethylene induced the production of the flavonoid phytoalexin, sakuranetin, but did not induce the production of a terpenoid phytoalexin, momilactone A. On the other hand, a free radical scavenger, Tiron, counteracted the induction of both sakuranetin and momilactone A production in methionine-treated leaves. Active oxygen species may be important in methionine-induced production of phytoalexins.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
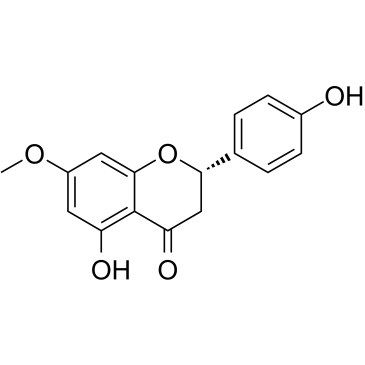 |
樱花亭
CAS:2957-21-3 |
C16H14O5 |
|
A nicotinic receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory effect of th...
2014-10-01 [Fitoterapia 98 , 11-21, (2014)] |
|
In vitro antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal activities of ...
2012-02-01 [Exp. Parasitol. 130(2) , 141-5, (2012)] |
|
Isoprenylated flavonoid and adipogenesis-promoting constitue...
2012-04-27 [J. Nat. Prod. 75(4) , 699-706, (2012)] |
|
Induced volatiles in elicitor-treated and rice blast fungus-...
2002-12-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66(12) , 2549-59, (2002)] |
|
O-demethylation and sulfation of 7-methoxylated flavanones b...
2003-02-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51(2) , 203-6, (2003)] |