| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
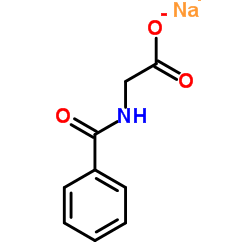 |
马尿酸钠 C9 H8 N NA O3
CAS:532-94-5 |
|
 |
马尿酸
CAS:495-69-2 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
马尿酸钠 C9 H8 N NA O3
CAS:532-94-5 |
|
 |
马尿酸
CAS:495-69-2 |