Environmental effects on charge densities of biologically active molecules: do molecule crystal environments indeed approximate protein surroundings?
Milena Mladenovic, Mario Arnone, Reinhold F Fink, Bernd Engels
文献索引:J. Phys. Chem. B 113(15) , 5072-82, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In the present paper, we investigate whether crystal and enzyme environments influence the electron density (ED) of active compounds in a similar manner. This supposition is essential for high-resolution X-ray studies, which use the EDs obtained from crystals of the pure active compound as approximations for the ED of the active compound in its complex with the target enzyme. The EDs of such complexes determine the molecular recognition process between the targeted enzyme and active compound and are, hence, extremely useful tools for rational drug design. The approximation of such EDs by data obtained from crystals of the pure active compound is needed since high-resolution X-ray experiments of the target-ligand complexes are still extremely demanding. Quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) and pure QM calculations are employed to determine the EDs of two inhibitors, the reversible trans-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid (AMCHA) and the irreversible E64c in four different environments (the enzyme-inhibitor complex, crystals of the pure compounds, a continuum solvation model, and the gas phase). Our investigation shows that the environment inside of the crystal of the pure active compound generally influences the ED of an active compound in a very similar way as the enzyme surrounding in the complex between the active compound and target enzyme. However, this does not hold any more if the geometrical arrangement of the inhibitor in the enzyme differs significantly from that in the crystal. While EDs computed for gas-phase environments deviate strongly from those in crystal and protein surroundings, polar solvent environments provide rather similar electron distributions. Thus, such continuum solvation models are very well suited to compute density databases which are to be employed for the determination of the ED of macromolecules.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
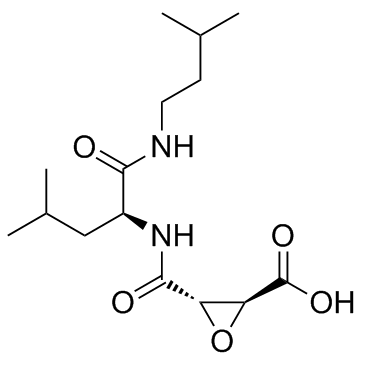 |
阿洛司他丁酸
CAS:76684-89-4 |
C15H26N2O5 |
|
Nitro/nitrosyl-ruthenium complexes are potent and selective ...
2014-10-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(10) , 6044-55, (2014)] |
|
HNA antibody-mediated neutrophil aggregation is dependent on...
2015-11-01 [Vox Sang. 109 , 366-74, (2015)] |
|
Structural basis for development of cathepsin B-specific non...
2002-06-03 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1597(2) , 244-51, (2002)] |
|
Primate neurons show different vulnerability to transient is...
2002-09-01 [Acta Neuropathol. 104(3) , 267-72, (2002)] |
|
A homologue of cathepsin L identified in conditioned medium ...
2006-07-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 71(4) , 444-9, (2006)] |