Pattern of polyamines and related monoacetyl derivatives in chick embryo retina during development.
G Taibi, M R Schiavo, G Calvaruso, G Tesoriere
文献索引:Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 12(5) , 423-9, (1994)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Polyamines and related monoacetyl derivatives were studied in chick embryo retina during development (6th-19th day). Putrescine, which is high in the first phase of retinogenesis, is necessary to sustain both tissue proliferation and via N-acetylputrescine, gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis. A later increase in spermidine and particularly spermine may play a role in the last phase of development when the retina reaches maturation. The presence of N1-acetylspermidine already at the 8th day indicates that in chick embryo retina, putrescine synthesis can depend on two separate pathways. The first involves ornithine decarboxylase activity; the second, spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase and probably polyamine oxidase that converts spermidine to putrescine via N1-acetylspermidine.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
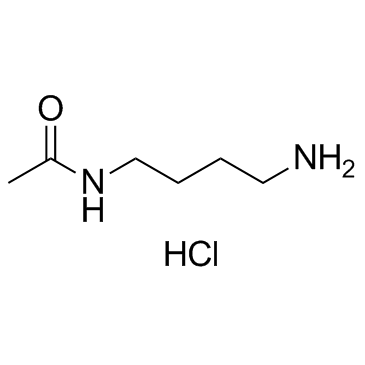 |
N-(4-氨基丁基)-乙酰胺
CAS:18233-70-0 |
C6H15ClN2O |
|
Correlation between endogenous polyamines in human cardiac t...
2016-02-01 [J. Cell. Mol. Med. 20 , 302-12, (2016)] |
|
Polyamine metabolism in Acanthamoeba culbertsoni.
1993-01-01 [Microbios 73(294) , 7-21, (1993)] |
|
Acetylated diamines inhibit endotoxin-induced lymphocyte act...
1984-04-01 [J. Immunol. 132(4) , 1888-91, (1984)] |
|
An improved gas chromatographic method for the determination...
1984-05-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 32(5) , 1878-84, (1984)] |
|
Serum polyamines in pre- and post-operative patients with br...
2009-01-18 [Cancer Lett. 273(2) , 300-4, (2009)] |