| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
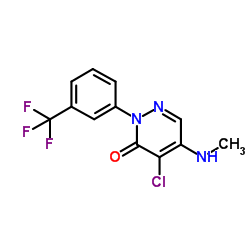 |
乙腈中氟草敏溶液
CAS:27314-13-2 |
|
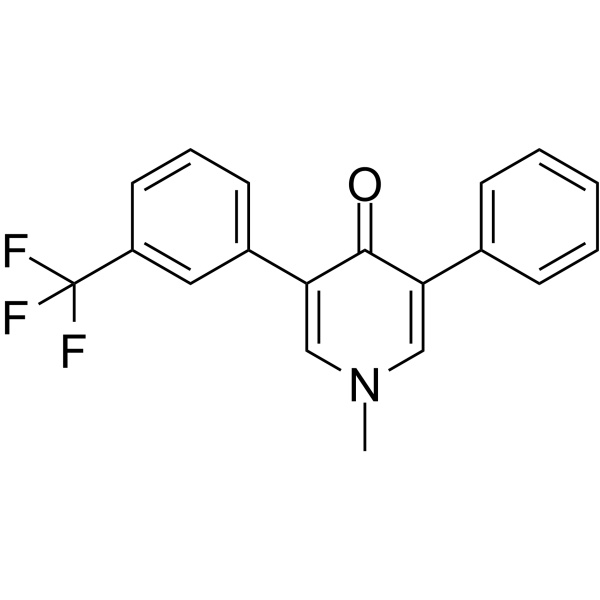 |
氟啶草酮
CAS:59756-60-4 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙腈中氟草敏溶液
CAS:27314-13-2 |
|
 |
氟啶草酮
CAS:59756-60-4 |