| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
A1受体促进剂,CHA
CAS:36396-99-3 |
|
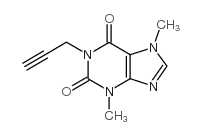 |
3,7-二甲基-1-炔丙基黄嘌呤
CAS:14114-46-6 |