| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
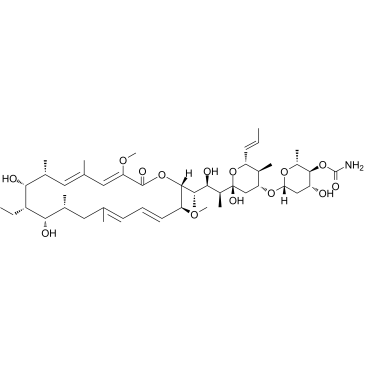 |
刀豆素A
CAS:80890-47-7 |
|
 |
五肽胃泌素
CAS:5534-95-2 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
刀豆素A
CAS:80890-47-7 |
|
 |
五肽胃泌素
CAS:5534-95-2 |