| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
2-甲基呋喃
CAS:534-22-5 |
|
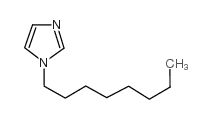 |
1-辛基咪唑
CAS:21252-69-7 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
2-甲基呋喃
CAS:534-22-5 |
|
 |
1-辛基咪唑
CAS:21252-69-7 |