| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
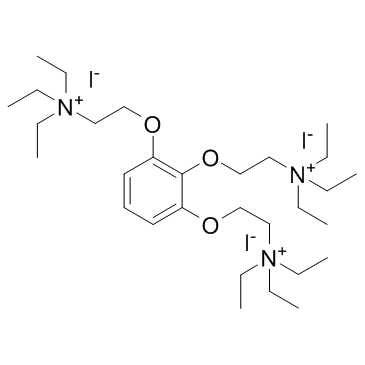 |
加拉碘铵
CAS:65-29-2 |
|
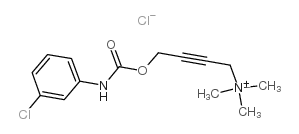 |
McN-A343,M1毒蕈碱激动剂
CAS:55-45-8 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
加拉碘铵
CAS:65-29-2 |
|
 |
McN-A343,M1毒蕈碱激动剂
CAS:55-45-8 |