Effects of linoleic and gamma-linolenic acids (efamol evening primrose oil) on fatty acid-binding proteins of rat liver.
A K Dutta-Roy, A C Demarco, S K Raha, J Shay, M Garvey, D F Horrobin
文献索引:Mol. Cell Biochem. 98(1-2) , 177-82, (1990)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We have studied the effects of Efamol evening primrose oil (EPO) on fatty acid-binding proteins (L-FABP) of rat liver. EPO contains 72% cis-linoleic acid and 9% cis-gamma linolenic acid. EPO has been clinically used for treatment of a number of diseases in humans and animals. EPO is also known to lower cholesterol level in humans and animals. Feeding of an EPO supplemented diet to rats (n = 9) for 2 months decreases the oleate binding capacity of purified L-FABP of rat liver whereas the palmitate binding activity was increased by 38%. However, EPO feeding did not alter the L-FABP concentrations significantly as measured by using the fluorescence fatty acid probe, dansylamino undecanoic acid. Endogenous fatty acid analysis of L-FABPs revealed significant qualitative and quantitative changes in fatty acid pattern after EPO feeding. EPO feeding decreased the endogenous palmitate level by 53% and oleate level by 64% in L-FABPs and also EPO feeding decreased the total endogenous fatty acid content from 62 nanomole per mg of protein to 42 nanomole per mg of L-FABP (n = 3).
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
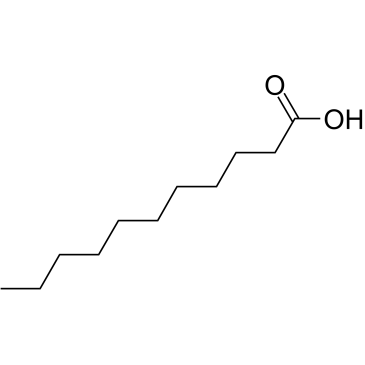 |
十一酸
CAS:112-37-8 |
C11H22O2 |
|
Use of multivariate statistical techniques to optimize the s...
2015-03-01 [Talanta 134 , 256-63, (2015)] |
|
Direct Derivatization vs Aqueous Extraction Methods of Fecal...
2015-07-01 [Lipids 50 , 681-9, (2015)] |
|
An efficient and economical MTT assay for determining the an...
2010-07-23 [J. Nat. Prod. 73 , 1193-5, (2010)] |
|
Chemical Modification of Graphene Oxide through Diazonium Ch...
2015-08-24 [Chemistry 21 , 12465-74, (2015)] |
|
Comparison of different protein immobilization methods on qu...
2001-12-15 [Anal. Biochem. 299(2) , 130-5, (2001)] |