A direct comparison of the taste of electrical and chemical stimuli.
David A Stevens, Diane Baker, Elizabeth Cutroni, Alexander Frey, David Pugh, Harry T Lawless
文献索引:Chem. Senses 33(5) , 405-13, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Three multidimensional scaling studies were conducted to compare the taste qualities evoked from electrical and chemical stimulation, including ferrous sulfate as a typical "metallic" taste stimulus. Bipolar, anodal, and cathodal stimulation were delivered by 1.5- or 3-V batteries applied to the tongue. Solutions of chemical stimuli including prototypical tastes and binary mixtures were evaporated on small metal disks to provide tactile impressions similar to those of the battery stimuli and avoid any potential response biases induced by the subjects' knowledge of the form of the stimulus. Multidimensional unfolding was performed to place stimuli and verbal descriptors in common perceptual spaces. Bipolar, anodal, and cathodal stimuli were tested in separate experiments but generated very similar perceptual spaces and were differentiated from the chemical stimuli. Electrical stimuli were associated with descriptors, such as metallic, copper penny, and iron nail, regardless of the polarity of stimulation. Taste qualities evoked by electric stimuli may not be fully described by commonly used taste stimuli or their binary mixtures and appear most adequately described by a unique metallic taste.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
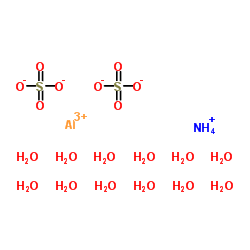 |
硫酸铝铵,十二水合物
CAS:7784-26-1 |
AlH31NO20S2 |
|
Aluminum ammonium sulfate dodecahydrate purified from tradit...
2012-06-01 [Biometals 25(3) , 541-51, (2012)] |
|
[A method for determining ammonium alum-based aerosol-formin...
1989-01-01 [Gig. Tr. Prof. Zabol. (2) , 46-7, (1989)] |
|
Removal of PCR inhibitors from soil DNA by chemical floccula...
2003-03-01 [J. Microbiol. Methods 52(3) , 389-93, (2003)] |
|
Evaluation of the reproductive and developmental toxicity of...
2011-09-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 49(9) , 1948-59, (2011)] |
|
Recovery of ammonium alum from waste solutions with a varyin...
2007-08-17 [J. Hazard. Mater. 147(1-2) , 342-9, (2007)] |