An endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis V583 responsible for the hydrolysis of high-mannose and hybrid-type N-linked glycans.
Liv Anette Bøhle, Geir Mathiesen, Gustav Vaaje-Kolstad, Vincent G H Eijsink
文献索引:FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 325(2) , 123-9, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
It has been demonstrated previously that Enterococcus faecalis produces secreted endoglycosidases that enable the bacteria to remove N-linked glycans from glycoproteins. One enzyme potentially responsible for this activity is EF0114, comprising a typical GH18 endoglycosidase domain and a GH20 domain. We have analyzed the other candidate, EF2863, and show that this predicted single domain GH18 protein is an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase. EF2863 hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond between two N-acetylglucosamines (GlcNAc) in N-linked glycans of the high-mannose and hybrid type, releasing the glycan and leaving one GlcNAc attached to the protein. The activity of EF2863 is similar to that of the well known deglycosylating enzyme EndoH from Streptomyces plicatus. According to the CAZy nomenclature, the enzyme is designated EfEndo18A.© 2011 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
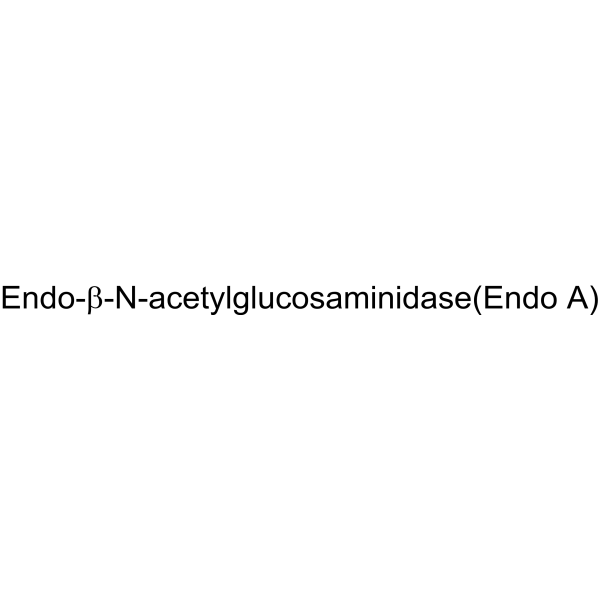 |
内切糖苷酶H 来源于褶皱链霉菌
CAS:37278-88-9 |
|
Improved plasma membrane expression of the trafficking defec...
2015-03-01 [Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 60 , 119-29, (2015)] |
|
A cholesterol consensus motif is required for efficient intr...
2015-01-15 [Biochem. J. 465(2) , 305-14, (2015)] |
|
Proteome analysis of the farnesol-induced stress response in...
2012-07-16 [J. Proteomics 75(13) , 4038-49, (2012)] |
|
The hepatitis C virus E1 glycoprotein undergoes productive f...
2011-01-01 [PLoS ONE 6(8) , e23838, (2011)] |
|
Double-knockout of putative endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (...
2011-01-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 75(5) , 1019-21, (2011)] |