| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
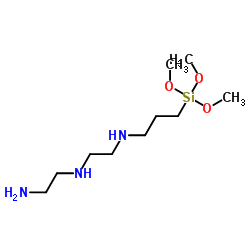 |
二乙烯三胺基丙基三甲氧基硅烷
CAS:35141-30-1 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
二乙烯三胺基丙基三甲氧基硅烷
CAS:35141-30-1 |