Influence of efrapeptin, aurovertin and citreoviridin on the mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase from Trypanosoma cruzi.
M A Cataldi de Flombaum, A O Stoppani
文献索引:Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 3(3) , 143-55, (1981)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Steady-state velocity studies using a substrate regenerating system showed that efrapeptin, citreoviridin and aurovertin inhibit both membrane-bound and soluble mitochondrial ATPase (coupling factor F1) from Trypanosoma cruzi. Maximal inhibitions of ATP hydrolysis produced by efrapeptin and citreoviridin were 100-93%, while the maximal inhibition produced by aurovertin was 40%. Half-maximal inhibitory concentrations decreased in the order citreoviridin greater than aurovertin greater than efrapeptin. Dissociation constants (KD) for the inhibitor-F1 complex were 81 nM (efrapeptin), 6.6 muM (aurovertin) and 40 muM (citreoviridin); KD values for the membrane-bound F1 were 2-4 fold higher than for soluble F1. Representation of efrapeptin inhibition data in the Hill form yielded straight lines (n = 1) while the same representation of citreoviridin inhibition yielded concave down plots. In contrast to the immediate effect of citreoviridin and aurovertin, efrapeptin inhibition was time-dependent. The onset of inhibition, which was pseudo-first-order with respect to efrapeptin, indicated that ATP may promote the binding of efrapeptin to the enzyme. The kinetics of ATP hydrolysis by T. cruzi ATPase as a function MgATP concentration could be explained by the presence of two substrate sites on the enzyme, interacting in such a way that the binding and catalytic events at one site were conformationally linked to the events at the other site, as with the mammalian ATPase. When the antibiotics were assayed at increasing substrate concentrations, efrapeptin produced a linear, mixed-type inhibition whereas citreoviridin produced a parabolic noncompetitive-type inhibition. The aurovertin effect was unusual since the extent of inhibition was greater at high substrate concentrations. Maximal concentrations of all the assayed antibiotics linearized the biphasic double reciprocal plot of control ATPase activity. Comparison of T. cruzi and mammalian F1 responses to the assayed antibiotics revealed the operation of similar inhibition mechanisms but the T. cruzi enzyme was significantly less sensitive to inhibitors than its mammalian counterpart.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
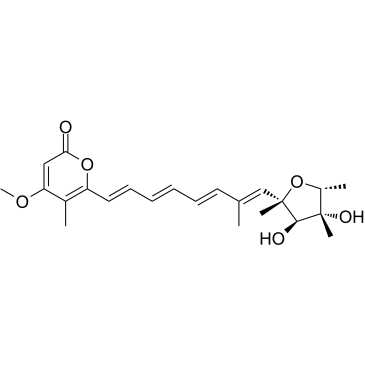 |
黄绿青霉素
CAS:25425-12-1 |
C23H30O6 |
|
Co-occurrence of aflatoxins B₁, B₂, G₁ and G₂, ochratoxin A,...
2012-01-01 [Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 29(4) , 694-703, (2012)] |
|
Production of citreoviridin by Penicillium citreonigrum stra...
2010-02-01 [Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 27(2) , 241-8, (2010)] |
|
Effect of citreoviridin and isocitreoviridin on beef heart m...
1989-05-01 [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 270(2) , 714-21, (1989)] |
|
Effect of citreoviridin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium citreo...
1981-01-01 [Toxicon 19(4) , 555-62, (1981)] |
|
In vitro inhibitory activity of citreoviridin against HIV-1 ...
1996-10-01 [J. Chemother. 8(5) , 351-7, (1996)] |