| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
维生素A酸; 视黄酸
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
 |
芳维甲酸
CAS:71441-28-6 |
|
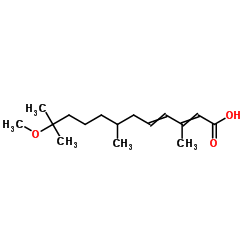 |
甲戊二烯酸
CAS:53092-52-7 |