Voltammetric detection of nitric oxide (NO) in the rat brain: its variations throughout the sleep-wake cycle.
S Burlet, R Cespuglio
文献索引:Neurosci. Lett. 226(2) , 131-5, (1997)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A sensor allowing the specific detection of nitric oxide (NO) is reported. Together with differential pulsed voltammetry, it allows the detection of a 650 mV signal either in NO solutions or in the rat frontal cortex. The intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of a NO donor (S-nitrosoglutathione, 20 mg/kg i.p.) increases the signal height (+30%) while that of a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor like L-nitro-arginine-p-nitro-anilide (100 mg/kg i.p.), produces its complete disappearance in the cortex of anesthetized rats. These results suggest that the 650 mV signal might be NO-dependent. Some other NOS inhibitors have been found either inefficient (L-nitro-arginine-methyl-ester) or partially efficient (7-nitro-indazole) on the signal height. In freely moving rats, also equipped with polygraphic electrodes, the signal measured in the frontal cortex exhibits the highest height during waking. It decreases during slow-wave sleep (-6%) and paradoxical sleep (-9%).
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
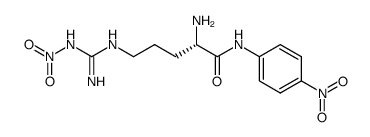 |
Nomega-硝基-L-精氨酸4-硝基苯胺氢溴酸盐
CAS:85697-89-8 |
C12H17N7O5 |
|
Monitoring nitric oxide (NO) in rat locus coeruleus: differe...
1997-04-14 [Neuroreport 8 , 1321-1325, (1997)] |
|
Effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on human arteries in ...
1996-01-01 [Br. J. Anaesth. 76(1) , 122-9, (1996)] |
|
Endogenous nitric oxide in the rat pons promotes sleep.
1999-01-16 [Brain Res. 816(1) , 209-19, (1999)] |
|
Stimulation of bradykinin B(1) receptors induces vasodilatio...
2000-04-18 [Circulation 101(15) , 1848-53, (2000)] |
|
NO in the caudal NTS modulates the increase in respiratory f...
2009-03-31 [Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 166(1) , 32-40, (2009)] |