Characterization of acrosin-like activity of lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) spermatozoa.
A Ciereszko, K Dabrowski, S I Ochkur
文献索引:Mol. Reprod. Dev. 45(1) , 72-7, (1996)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Acipenserid fish sperm possess trypsin-like activity, resembling acrosin activity of mammalian sperm, which can be measured by hydrolysis of N-alpha-benzoyl-DL-arginine p-nitroanilide (BAPNA) (Ciereszko et al., 1994: J Exp Zool 268:486-491). We found that this activity can be preserved when sperm is frozen on dry ice with 0.6 M sucrose-10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) extender (sperm:extender ratio 1:3), and subsequently stored in liquid nitrogen. However, other methods of freezing (without cryoprotectant at -18 degrees C, -80 degrees C, and -196 degrees C) did not protect this activity. Acrosin-like activity decreased in the course of storage of milt on ice; 88% decline was recorded after 13 days. Acrosin-like activity increased with temperature from 10 degrees C to 30 degrees C, but was inactivated at 40 degrees C to about 40% as compared to the optimum temperature. Triton X-100 inhibited activity by 15% and 72% at 0.01% and 0.1% concentrations, respectively. Activity was not affected by Mg2+ but was inhibited by Zn2+ (30% and 75% in the presence of 0.1 mM and 1 mM, respectively). Maximum velocity of substrate hydrolysis was observed at 2 mM of BAPNA. Acrosin-like activity was effectively inhibited by 4'-acetamidophenyl 4-guanidinobenzoate (AGB), an inhibitor of mammalian acrosin. Sperm acrosin-like activity correlated negatively with antiproteinase activity of seminal plasma. We conclude that sturgeon acrosin-like activity shares many properties with mammalian acrosin. On the other hand, it has some unique properties which may represent adaptations of this enzyme to the environment of external fertilization.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
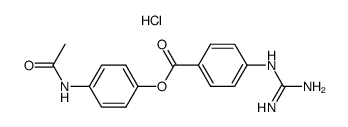 |
4'-ACETAMIDOPHENYL 4-GUANIDINOBENZOATE HYDROCHLORIDE
CAS:79119-49-6 |
C16H17ClN4O3 |
|
Inhibition of a tumour protease with 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin...
1994-01-01 [J. Enzym. Inhib. 8(3) , 213-21, (1994)] |
|
Synthesis and inhibition of human acrosin and trypsin and ac...
1986-04-01 [J. Med. Chem. 29 , 514, (1986)] |
|
Trypsin inhibitors prevent the progesterone-initiated increa...
1991-06-01 [J. Exp. Zool. 258(3) , 384-93, (1991)] |
|
Inhibition of the human sperm acrosome reaction by proteinas...
1989-08-01 [Gamete Res. 23(4) , 387-97, (1989)] |
|
Acrosin inhibitor, 4'-acetamidophenyl 4-guanidinobenzoate, a...
1995-05-01 [Contraception 51(5) , 319-22, (1995)] |