Selection of DNA aptamers against polychlorinated biphenyls as potential biorecognition elements for environmental analysis.
Shengmin Xu, Hang Yuan, Shaopeng Chen, An Xu, Jun Wang, Lijun Wu
文献索引:Anal. Biochem. 423(2) , 195-201, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have been of major concerns for decades due to their potential toxicity to human health. To trace the PCBs efficiently and sensitively, many detection methods have been developed. Aptamers, a new class of diagnostic tools, are considered to be such additional candidates for detection of pollutants. In the current study, we report the DNA aptamers, isolated by FluMag-SELEX (a modified SELEX [systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment] technology), that recognize PCBs with the dissociation constants (Kd values) down to the micromolar range. Using the selected aptamers, a highly sensitive aptamer-based fluorescent assay for detection of PCBs was established using gold nanoparticles, with a widely linear range from 0.1 to 100 ng/ml. Moreover, our aptamer-based gold nanoprobe displays specificity toward 3,3',4,4'-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB77) compared with a few common PCB77 structural analogs. These results open the possibility of using aptamers as biorecognition elements for easy and fast environmental monitoring.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
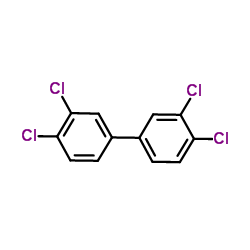 |
3,3',4,4'-四氯联苯
CAS:32598-13-3 |
C12H6Cl4 |
|
Polychlorinated biphenyl 77 augments angiotensin II-induced ...
2011-11-15 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 257(1) , 148-54, (2011)] |
|
Biotransformation of 2,2',5,5'-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB 52) ...
2011-05-16 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 24(5) , 718-25, (2011)] |
|
Differential sensitivity of CYP1A to 3,3',4',4-tetrachlorobi...
1998-05-01 [Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 152(1) , 42-50, (2010)] |
|
Lack of CYP1A responsiveness in species inhabiting chronical...
2013-03-01 [Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 157(2) , 212-9, (2013)] |
|
Identification and mRNA expression of pi-class glutathione S...
2012-03-01 [Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 155(2) , 300-6, (2012)] |