| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
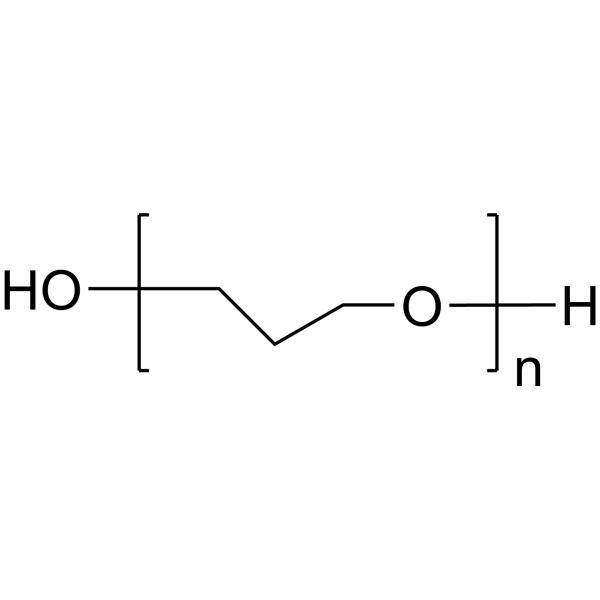 |
聚乙二醇
CAS:25322-68-3 |
|
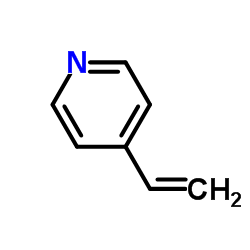 |
4-乙烯基吡啶
CAS:100-43-6 |
|
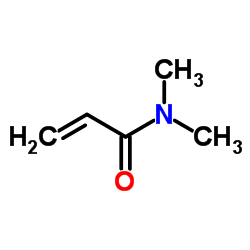 |
N,N-二甲基丙烯酰胺
CAS:2680-03-7 |
|
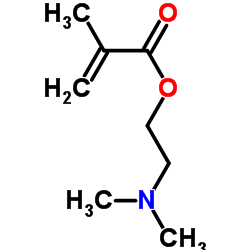 |
甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯
CAS:2867-47-2 |