| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
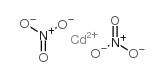 |
硝酸镉
CAS:10325-94-7 |
|
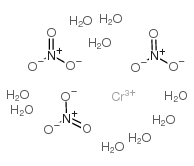 |
硝酸铬(III) 九水合物
CAS:7789-02-8 |
|
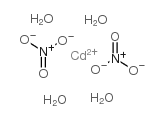 |
硝酸镉,四水合物
CAS:10022-68-1 |