Catanionic surfactant vesicles for electrostatic molecular sequestration and separation.
Sara B Lioi, Xiang Wang, Mohammad R Islam, Emily J Danoff, Douglas S English
文献索引:Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(41) , 9315-25, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Mixtures of oppositely charged surfactants, commonly called catanionic mixtures, are one of the most interesting and promising areas of colloidal chemistry. In this paper we review our previous work and report new results on electrostatic adsorption of organic solutes and DNA to the exterior surfaces of catanionic, unilamellar vesicles which form spontaneously in mixtures of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS) and cetyltrimethylammonium tosylate (CTAT). Our group, along with others, has shown that organic ions and polyelectrolytes will bind to the exterior surface of oppositely charged catanionic vesicles through interactions with unpaired ionic surfactants present in the vesicle bilayer. The electrostatic sequestration of organic ions with catanionic vesicles is extremely efficient with excellent long-term stability and can be used to perform separations on mixtures of charged organic solutes. Using regular solution theory extended to vesicle-forming surfactant mixtures, we can understand how the composition of the bilayer changes with surfactant dilution, and we study this effect using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS). We employ FCS to make sensitive measurements of bilayer adsorption and compare the adsorption of a small molecular probe with that of a single-stranded, dye-labeled DNA molecule. From these FCS studies, adsorption isotherms can be obtained that report on the relative binding strengths of the two systems. The results show that DNA binds much more strongly to the exterior surface of positively charged catanionic vesicles, and can even stabilize vesicles at very low surfactant concentrations near the critical aggregation concentration (cac).
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
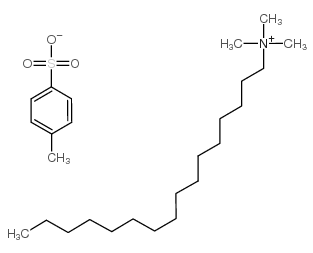 |
十六烷基三甲基对甲苯磺酸铵
CAS:138-32-9 |
C26H49NO3S |
|
Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for potential deliv...
2014-11-07 [Dalton Trans. 43(41) , 15482-90, (2014)] |
|
Engineering poly(ethylene glycol) particles for improved bio...
2015-02-24 [ACS Nano 9(2) , 1571-80, (2015)] |
|
Dispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes of narrow diame...
2005-08-04 [J. Phys. Chem. B 109 , 14454, (2005)] |
|
[Analysis of a new toothpaste].
[Odontostomatol. Implantoprotesi (4) , 17-9, (1981)] |
|
Spontaneous vesicle formation in aqueous mixtures of single-...
1989-09-22 [Science 245(4924) , 1371-4, (1989)] |