A heptaketide naphthaldehyde produced by a polyketide synthase from Nectria haematococca.
Takayoshi Awakawa, Takuya Kaji, Toshiyuki Wakimoto, Ikuro Abe
文献索引:Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22(13) , 4338-40, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Bostrycoidin and fusarubin are biologically active fungal polyketides produced by Nectria haematococca. This azaanthraquinone and naphthoquinone are thought to be biosynthesized via formation of a C(14) heptaketide aldehyde as a common key intermediate. A BLAST search against the genome of N. haematococca revealed one candidate gene (NECHADRAFT_101778, NhPKS1), which encodes a multi-domain polyketide synthase (PKS) with a thiol reductase (TR) domain that would facilitate the reductive release of the intermediate to produce a free aldehyde. To investigate the possible involvement of NhPKS1 in the biosynthesis of bostrycoidin and fusarubin, NhPKS1 was heterologously expressed in Aspergillus oryzae, and shown to produce a heptaketide 3-acetonyl-1,6,8-trihydroxy-2-naphthaldehyde as a single product. Thus, NhPKS1 catalyzes a C-2/C-11 and C-4/C-9 aldol-type cyclization of a linear intermediate followed by a subsequent reductive product release to yield the naphthaldehyde. The results indicate NhPKS1 is the enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of bostrycoidin and fusarubin.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
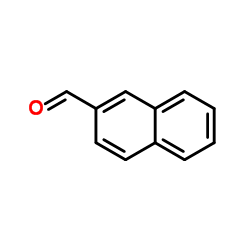 |
2-萘甲醛
CAS:66-99-9 |
C11H8O |
|
Studies on structure-activity relationship of gossypol, goss...
1986-05-01 [Contraception 33(5) , 519-28, (1986)] |
|
Naphthaldehydes as reversible inhibitors of rat hepatic aryl...
1993-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 21(2) , 400-2, (1993)] |
|
pH-Responsive polymeric micelles based on amphiphilic chitos...
2016-01-30 [Int. J. Pharm. 497 , 150-60, (2016)] |
|
Enantioselective Addition of Diethylzinc to Aldehydes Cataly...
2016-01-01 [Chirality 28 , 65-71, (2016)] |
|
Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in L-1210 murin...
2010-09-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 62(9) , 1128-36, (2010)] |