| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
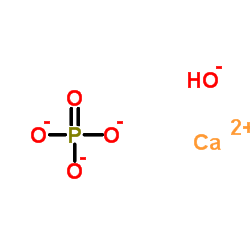 |
羟基磷灰石
CAS:1306-06-5 |
|
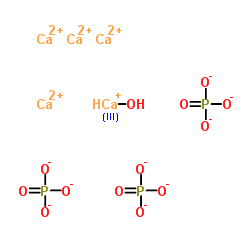 |
磷酸钙
CAS:12167-74-7 |
|
 |
氮化硼
CAS:10043-11-5 |