| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
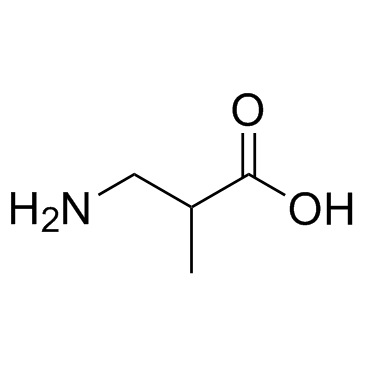 |
DL-3-氨基异丁酸
CAS:144-90-1 |
|
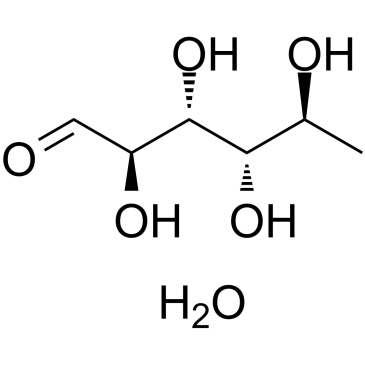 |
L-鼠李糖
CAS:10030-85-0 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
DL-3-氨基异丁酸
CAS:144-90-1 |
|
 |
L-鼠李糖
CAS:10030-85-0 |