Species-dependent effects of the phenolic herbicide ioxynil with potential thyroid hormone disrupting activity: modulation of its cellular uptake and activity by interaction with serum thyroid hormone-binding proteins.
Sakura Akiyoshi, Gobun Sai, Kiyoshi Yamauchi
文献索引:J. Environ. Sci. (China) 24(5) , 949-55, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Ioxynil, a phenolic herbicide, is known to exert thyroid hormone (TH) disrupting activity by interfering with TH-binding to plasma proteins and a step of the cellular TH-signaling pathway in restricted animal species. However, comparative studies are still lacking on the TH disruption. We investigated the interaction of [125I]ioxynil with serum proteins from rainbow trout, bullfrog, chicken, pig, rat, and mouse, using native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Candidate ioxynil-binding proteins, which included lipoproteins, albumin and transthyretin (TTR), differed among the vertebrates tested. Rainbow trout and bullfrog tadpole serum had the lowest binding activity for ioxynil, whereas the eutherian serum had the highest binding activity. The cellular uptake of, and response to, ioxynil were suppressed by rat serum greater than by tadpole serum. The cellular uptake of [125I]ioxynil competed strongly with phenols with a single ring, but not with THs. Our results suggested that ioxynil interferes with TH homeostasis in plasma and with a step of cellular TH-signaling pathway other than TH-uptake system, in a species-specific manner.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
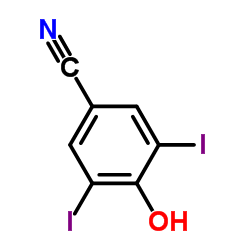 |
4-羟基-3,5-二碘苯腈
CAS:1689-83-4 |
C7H3I2NO |
|
Microbial degradation of the benzonitrile herbicides dichlob...
2008-07-01 [Environ. Pollut. 154(2) , 155-68, (2008)] |
|
High-performance liquid chromatographic study of the aromati...
1996-05-31 [J. Chromatogr. B, Biomed. Appl. 681(1) , 191-5, (1996)] |
|
The effect of endocrine disrupting chemicals on thyroid horm...
2003-10-15 [Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 134(1) , 36-43, (2003)] |
|
Mutation in phenol-type herbicide resistance maps within the...
1989-03-27 [FEBS Lett. 246(1-2) , 207-10, (1989)] |
|
Ioxynil and 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine: comparison of binding t...
1988-12-01 [Toxicol. Lett. 44(3) , 281-7, (1988)] |