| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
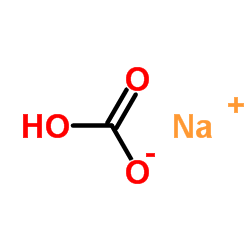 |
碳酸氢钠
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
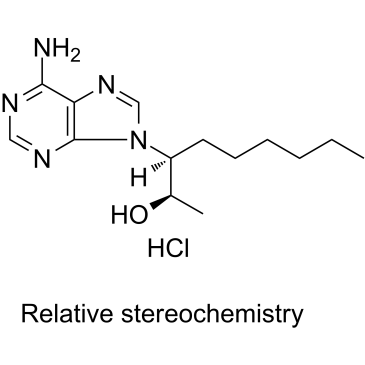 |
外消旋-9-(2-羟基-3-壬基)腺嘌呤盐酸盐
CAS:58337-38-5 |
|
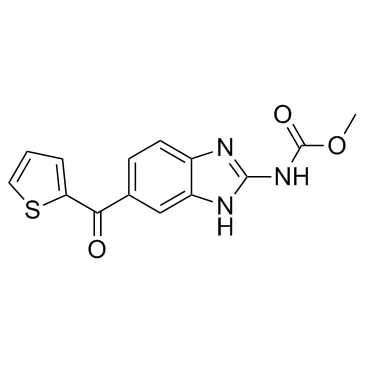 |
诺考达唑
CAS:31430-18-9 |