| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
胆固醇氧化酶
CAS:9028-76-6 |
|
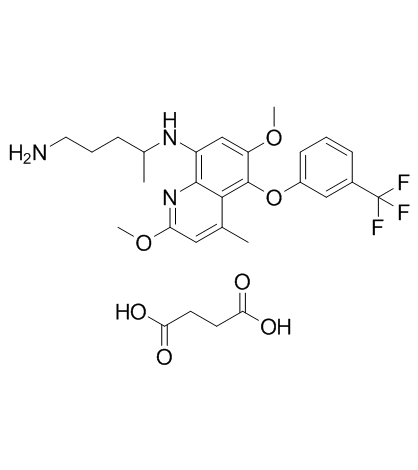 |
Tafenoquine Succinate
CAS:106635-81-8 |