Up- and down-regulation of Fragaria x ananassa O-methyltransferase: impacts on furanone and phenylpropanoid metabolism.
Stefan Lunkenbein, Elma M J Salentijn, Heather A Coiner, Marjan J Boone, Frans A Krens, Wilfried Schwab
文献索引:J. Exp. Bot. 57(10) , 2445-53, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A complex mixture of hundreds of substances determines strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa) aroma, but only approximately 15 volatiles are considered as key flavour compounds. Of these, 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (HDMF) is regarded as the most important, but it is methylated further by FaOMT (Fragaria x ananassa O-methyltransferase) to 2,5-dimethyl-4-methoxy-3(2H)-furanone (DMMF) during the ripening process. It is shown here that transformation of strawberry with the FaOMT sequence in sense and antisense orientation, under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter, resulted in a near total loss of DMMF, whereas the levels of the other volatiles remained unchanged. FaOMT repression also affected the ratio of feruloyl 1-O-beta-D-glucose and caffeoyl 1-O-beta-D-glucose, indicating a dual function of the enzyme in planta. Thus, FaOMT is involved in at least two different biochemical pathways in ripe strawberry fruit.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
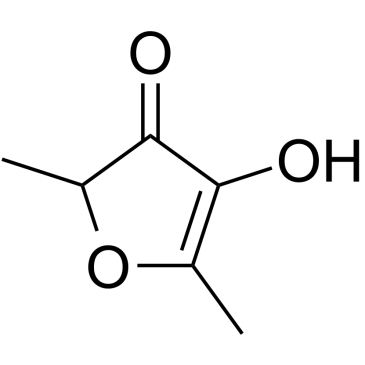 |
2,5-二甲基-4-羟基-3(2H)-呋喃酮
CAS:3658-77-3 |
C6H8O3 |
|
Odorants in breast milk.
2003-10-01 [Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 157(10) , 1031, (2003)] |
|
Structural basis for the enzymatic formation of the key stra...
2013-06-07 [J. Biol. Chem. 288(23) , 16815-26, (2013)] |
|
Characterization of the key aroma compounds in soy sauce usi...
2007-07-25 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 55(15) , 6262-9, (2007)] |
|
Effects of water-soluble natural antioxidants on photosensit...
2008-05-01 [J. Food Sci. 73(4) , C256-61, (2008)] |
|
Quantification of 2,5-dimethyl-4-hydroxy-3(2H)-furanone usin...
2008-10-24 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1208(1-2) , 197-201, (2008)] |