| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
单响尾蛇毒蛋白
CAS:315-22-0 |
|
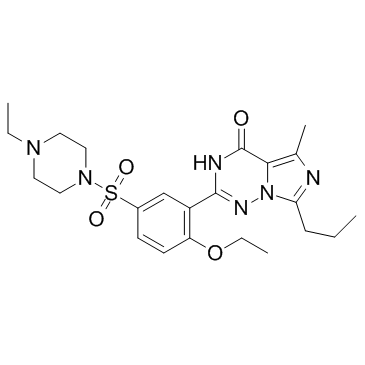 |
伐地那非
CAS:224785-90-4 |
|
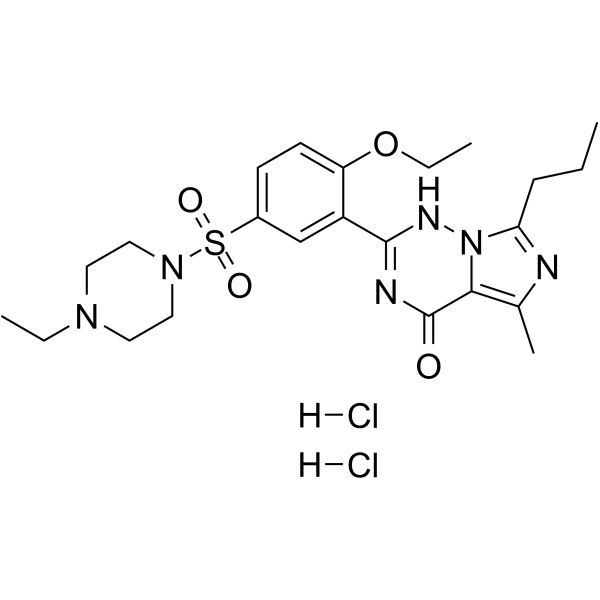 |
伐地那非
CAS:224789-15-5 |