Switching of polymerization activity of cinnamoyl-alpha-cyclodextrin.
Motofumi Osaki, Yoshinori Takashima, Hiroyasu Yamaguchi, Akira Harada
文献索引:Org. Biomol. Chem. 7(8) , 1646-51, (2009)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Cinnamoyl alpha-cyclodextrin (alpha-CD) has been found to initiate polymerization of delta-valerolactone (delta-VL) to give a polymer in high yield. By the presence of the cinnamoyl group, hydrogen bond was formed between the carbonyl oxygen of delta-VL and the hydroxyl group of CD to activate the monomer, which was observed by FT-IR measurements. However, the cinnamoyl group at the C(3)- and C(6)-positions of alpha-CD did not affect the polymerization ability. Only that of the C(2)-position showed high polymerization activity. The polymerization activity could be switched by the photoisomerization of the cinnamoyl group attached to the rim of alpha-CD. Specific monomer recognition and polymerization in the active site of the alpha-CD cavity was changed by the photoisomerization.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
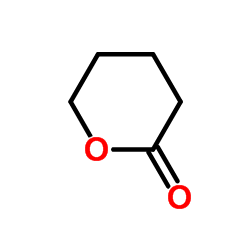 |
δ-戊内酯
CAS:542-28-9 |
C5H8O2 |
|
Antimicrobial properties of Kalanchoe blossfeldiana: a focus...
2015-07-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67 , 951-62, (2015)] |
|
Characterization of the PON1 active site using modeling simu...
2008-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 7504-9, (2008)] |
|
5- and 6-membered (thio)lactones are prodrug type carbonic a...
2012-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22 , 267-70, (2012)] |
|
High affinity, stability, and lactonase activity of serum pa...
2005-09-06 [Biochemistry 44(35) , 11843-54, (2005)] |
|
In vitro degradation and dissolution behaviours of microsphe...
2000-01-01 [J. Microencapsul. 17(5) , 577-86, (2000)] |