| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
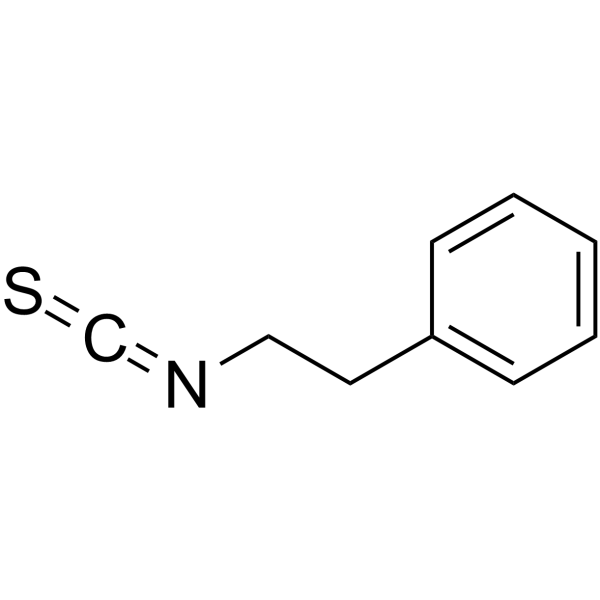 |
异硫氰酸-2-苯乙酯
CAS:2257-09-2 |
|
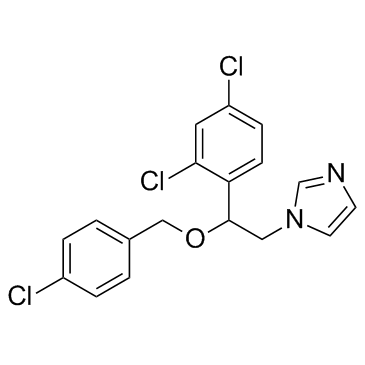 |
益康唑
CAS:27220-47-9 |
|
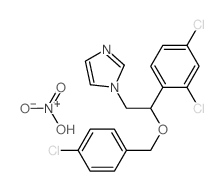 |
硝酸益康唑
CAS:68797-31-9 |