| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
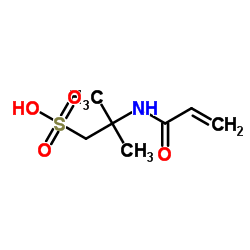 |
2-丙烯酰胺基-2-甲基丙磺酸
CAS:15214-89-8 |
|
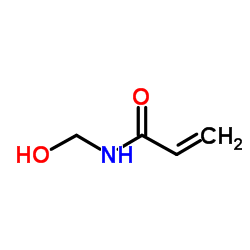 |
N-羟甲基丙烯酰胺
CAS:924-42-5 |
|
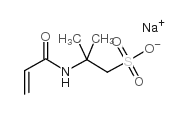 |
2-丙烯酰胺基-2-甲基丙磺酸 钠盐 溶液
CAS:5165-97-9 |