Cellular membranes, the sites for the antifungal activity of the herbicide sethoxydim.
B S Pakdaman, E Mohammadi Goltapeh, R Sepehrifar, M Pouriesa, M Rahimi Fard, F Moradi, S A M Modarres
文献索引:Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 10(15) , 2480-4, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The fungicidal effect of sethoxydim on the canola (Brassica napus var. Olifera) white stem rot pathogen (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) encouraged us to conduct a series of studies on the mechanism of the antifungal activity of this herbicide commonly applied in Iranian fields under canola cultivation. Present preliminary studies on the changes in the level of Malondialdehyde (MDA) as the main product generated through peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids indicated the disintegration of the fungal bilayer of plasma membrane as the result of the herbicidal treatment. Also, it was demonstrated that the amount of hydrogen peroxide in the treated samples was higher than the control samples with no herbicidal treatment. Therefore, our present results confirm the disintegration of the plasma membrane as one of the mechanism for the antifungal impact of sethoxydim. As with weed plants, the phytotoxic impact of this herbicide has been attributed to the inhibition of the first enzyme in the lipid biosynthesis pathway, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, therefore, it would be very interesting to study on this subject and the relations between the sensitivity of different fungi and their DNA and protein sequences of acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
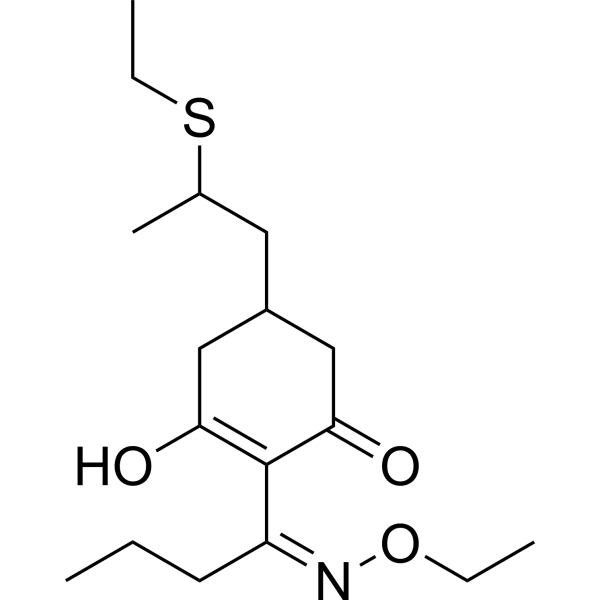 |
稀禾定
CAS:74051-80-2 |
C17H29NO3S |
|
Effects of herbicides on Behr's metalmark butterfly, a surro...
2012-05-01 [Environ. Pollut. 164 , 24-7, (2012)] |
|
Inhibition of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase by sethoxy...
1999-02-22 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 9(4) , 551-4, (1999)] |
|
Trypanosoma brucei: inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by ...
2012-02-01 [Exp. Parasitol. 130(2) , 159-65, (2012)] |
|
A novel W1999S mutation and non-target site resistance impac...
2013-01-01 [PLoS ONE 8 , e58012, (2013)] |
|
Genome sequence of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) provides...
2012-06-01 [Nat. Biotechnol. 30(6) , 549-54, (2012)] |