Retinoid X receptor-selective ligands produce malformations in Xenopus embryos.
S Minucci, J P Saint-Jeannet, R Toyama, G Scita, L M DeLuca, M Tiara, A A Levin, K Ozato, I B Dawid
文献索引:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93(5) , 1803-7, (1996)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Retinoids exert pleiotropic effects on the development of vertebrates through the action of retinoic acid receptors (RAR) and retinoid X receptors (RXR). We have investigated the effect of synthetic retinoids selective for RXR and RAR on the development of Xenopus and zebrafish embryos. In Xenopus, both ligands selective for RAR and RXR caused striking malformations along the anterior-posterior axis, whereas in zebrafish only ligands specific for RAR caused embryonic malformations. In Xenopus, RAR- and RXR-selective ligands regulated the expression of the Xlim-1, gsc, and HoxA1 genes similarly as all-trans-retinoic acid. Nevertheless, RXR-selective ligands activated only an RXR responsive reporter but not an RAR responsive reporter introduced by microinjection into the Xenopus embryo, consistent with our failure to detect conversion of an RXR-selective ligand to different derivatives in the embryo. These results suggest that Xenopus embryos possess a unique response pathway in which liganded RXR can control gene expression. Our observations further illustrate the divergence in retinoid responsiveness between different vertebrate species.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
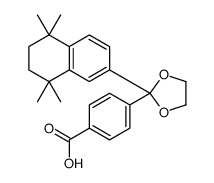 |
SR 11237,泛RXR激动剂
CAS:146670-40-8 |
C24H28O4 |
|
Retinoids Bias Integrin Expression and Function in Cutaneous...
2015-08-01 [J. Invest. Dermatol. 135 , 2102-8, (2015)] |
|
Pharmacological evaluation of the mechanisms involved in inc...
2016-03-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 294 , 32-42, (2016)] |
|
Detection of a receptor-ligand non-covalent complex using a ...
2002-01-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 16(20) , 2003-6, (2002)] |
|
The "Phantom Effect" of the Rexinoid LG100754: structural an...
2010-01-01 [PLoS ONE 5(11) , e15119, (2010)] |
|
Retinoids and rexinoids inhibit hepatitis C virus independen...
2014-02-01 [Microbes Infect. 16(2) , 114-22, (2014)] |