Transport behavior of 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine in a freshwater estuary.
Marianne C Nyman, Kirby McCord, William L Wood, Ernest R Blatchley
文献索引:Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 22(1) , 20-5, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Like many hydrophobic organic compounds, 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine (DCB) partitions preferentially to (sediment) particles in lake systems. As such, the behavior of DCB in these systems is substantially affected by the movement of sediments. A field investigation of DCB distribution in sediments of Lake Macatawa (Holland, MI, USA) was initiated. The pattern of DCB distribution within the lake was found to display an oscillatory pattern that was consistent with a wind-driven mechanism of sediment transport. Numerical modeling of seiching behavior supported the hypothesized importance of this mechanism of sediment transport and redistribution. The dynamic behavior of sediment-associated DCB within Lake Macatawa seems to be strongly influenced by phenomena that are common to many freshwater estuaries. As such, the behavior of this system is expected to represent a reasonable model of the dynamic behavior of hydrophobic contaminants in other freshwater estuaries.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
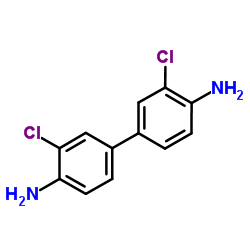 |
3,3′-二氯联苯胺
CAS:91-94-1 |
C12H10Cl2N2 |
|
Evidence that 4-aminobiphenyl, benzidine, and benzidine cong...
2007-06-01 [Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 48(5) , 404-13, (2007)] |
|
Photodechlorination of 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine in water.
2002-03-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 21(3) , 500-6, (2002)] |
|
Determination of dichlorobenzidine-hemoglobin adducts by GC/...
1997-01-01 [Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 69(4) , 240-6, (1997)] |
|
Sorption of benzidine and 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine to lake sed...
2005-05-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 24(5) , 1022-8, (2005)] |
|
Identification of a new mutagen, 4,4'-diamino-3,3'-dichloro-...
2008-01-01 [Mutat. Res. 655(1-2) , 28-35, (2008)] |