| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
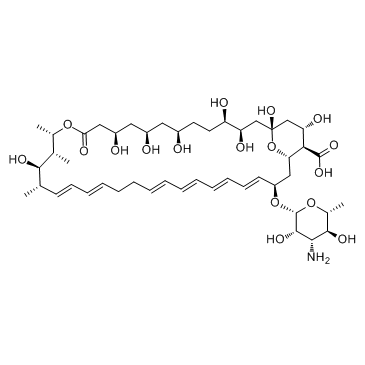 |
制霉菌素
CAS:1400-61-9 |
|
 |
亚硒酸钠
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
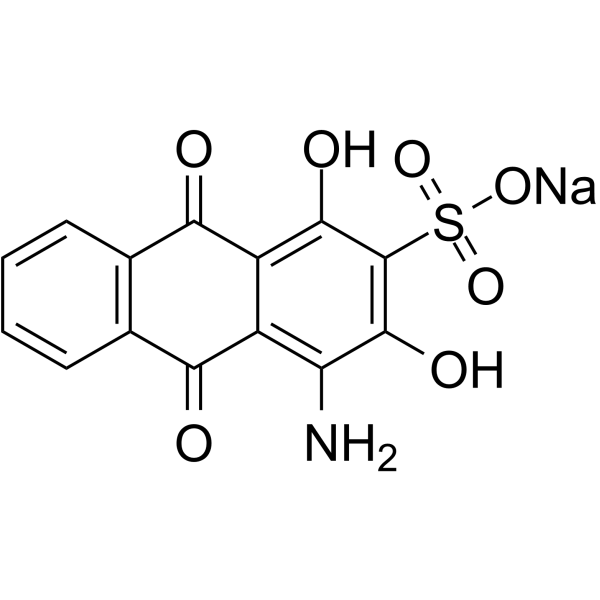 |
核固红
CAS:6409-77-4 |
|
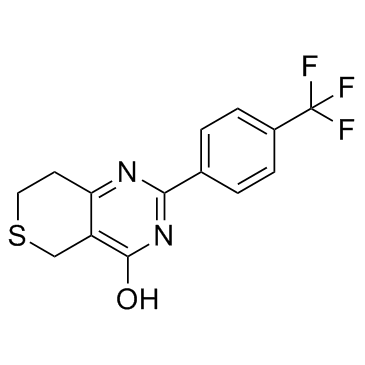 |
XAV-939
CAS:284028-89-3 |