| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
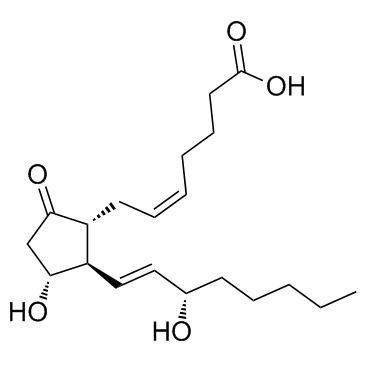 |
地诺前列酮
CAS:363-24-6 |
|
 |
4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
列腺素 E1
CAS:745-65-3 |
|
 |
谷胱甘肽/5-L-谷氨酰-L-半胱氨酰甘氨酸
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
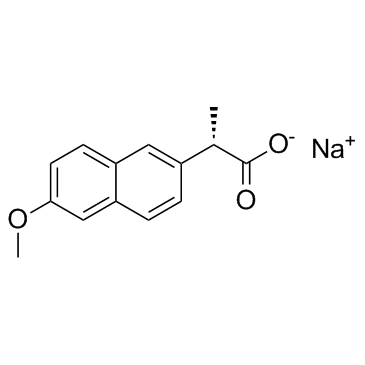 |
萘普生钠
CAS:26159-34-2 |
|
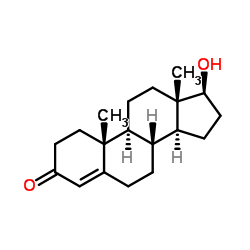 |
睾酮
CAS:58-22-0 |
|
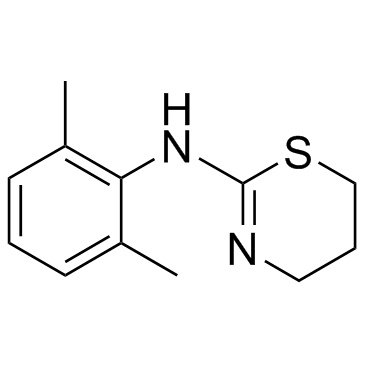 |
赛拉嗪
CAS:7361-61-7 |