Engineering novel cell surface receptors for virus-mediated gene transfer.
J H Lee, T J Baker, L K Mahal, J Zabner, C R Bertozzi, D F Wiemer, M J Welsh
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 274(31) , 21878-84, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The absence of viral receptors is a major barrier to efficient gene transfer in many cells. To overcome this barrier, we developed an artificial receptor based on expression of a novel sugar. We fed cells an unnatural monosaccharide, a modified mannosamine that replaced the acetyl group with a levulinate group (ManLev). ManLev was metabolized and incorporated into cell-surface glycoconjugates. The synthetic sugar decorated the cell surface with a unique ketone group that served as a foundation on which we built an adenovirus receptor by covalently binding biotin hydrazide to the ketone. The artificial receptor enhanced adenoviral vector binding and gene transfer to cells that are relatively resistant to adenovirus infection. These data are the first to suggest the feasibility of a strategy that improves the efficiency of gene transfer by using the biosynthetic machinery of the cell to engineer novel sugars on the cell surface.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
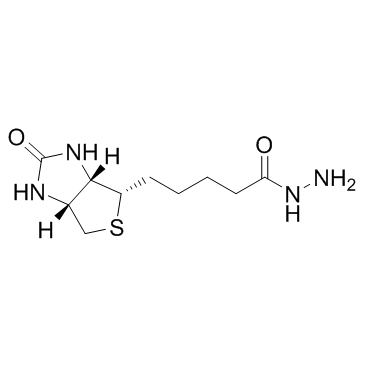 |
生物素酰肼
CAS:66640-86-6 |
C10H18N4O2S |
|
Sensitive chemiluminescent imaging for chemoselective analys...
2012-02-07 [Anal. Chem. 84(3) , 1452-8, (2012)] |
|
Determining the effects of antioxidants on oxidative stress ...
2011-12-15 [Anal. Chem. 83(24) , 9328-36, (2011)] |
|
Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of derivatization re...
2013-09-07 [Analyst 138(17) , 5081-8, (2013)] |
|
Substrate profiling of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B by...
2007-05-02 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(17) , 5366-7, (2007)] |
|
Comparing the efficiencies of hydrazide labels in the study ...
2012-09-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 404(5) , 1399-411, (2012)] |