| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
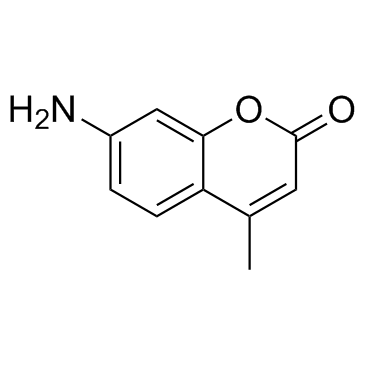 |
7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素
CAS:26093-31-2 |
|
 |
重组肠激酶
CAS:9014-74-8 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素
CAS:26093-31-2 |
|
 |
重组肠激酶
CAS:9014-74-8 |