Metabolism of uniconazole-P in water-sediment systems under illumination.
Rika Kodaka, Terumi Sugano, Toshiyuki Katagi
文献索引:Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 25(2) , 310-6, (2006)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Aerobic soil metabolism of uniconazole-P ([S]-E-1-[4-chlorophenyl]-4,4-dimethyl-2-[1,2,4-triazole-1-yl]-penten-3-ol) and the effect of illumination on metabolic profiles were studied in the water-sediment system when spiked to water. Uniconazole-P was gradually partitioned to the sediment with an aquatic half-life of 6.9 d in darkness with formation of bound residues. Illumination of the system from a xenon lamp (>290 nm) greatly accelerated the degradation of uniconazole-P via photoinduced isomerization between E- and Z-isomers with a subsequent intramolecular cyclization, and its aquatic half-life was greatly reduced to 0.6 d. Kinetic analysis based on compartment models suggested the possible contribution of photodegradation at the water-sediment interface, leading to more formation of the cyclized derivative in the sediment.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
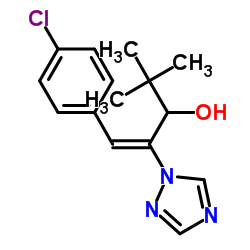 |
烯效唑
CAS:83657-22-1 |
C15H18ClN3O |
|
Improved biological effects of uniconazole using porous holl...
2012-03-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 68(3) , 437-43, (2012)] |
|
Formation of embryogenic cell clumps from carrot epidermal c...
2005-01-01 [J. Plant Physiol. 162(1) , 47-54, (2005)] |
|
Enantiomeric resolution and growth-retardant activity in ric...
2012-01-11 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(1) , 160-4, (2012)] |
|
Involvement of gibberellin in tracheary element differentiat...
2006-09-01 [Protoplasma 228(4) , 179-87, (2006)] |
|
Plants with increased expression of ent-kaurene oxidase are ...
2005-02-01 [Plant Cell Physiol. 46(2) , 284-91, (2005)] |