| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
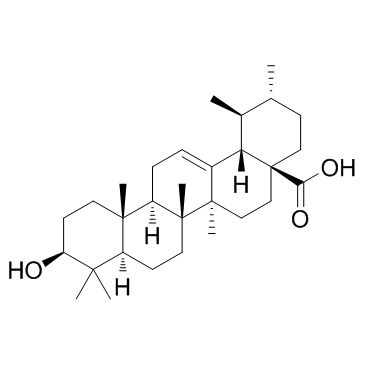 |
熊果酸
CAS:77-52-1 |
|
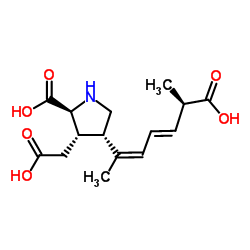 |
软骨藻酸
CAS:14277-97-5 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
熊果酸
CAS:77-52-1 |
|
 |
软骨藻酸
CAS:14277-97-5 |