Inhibition of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase augments cardiac injury by H2O2
Guro Valen, Anne G. Semb, Jarle Vaage
文献索引:Free Radic. Biol. Med. 15(1) , 27-35, (1993)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The role of arachidonic acid metabolites in the cardiac effects of toxic oxygen metabolites (TOM) was investigated in buffer-perfused rat hearts (Langendorff model). Hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2, 200 μM) was given for 10 min to generate TOM, followed by 30 min recovery. H 2O 2 reduced left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP), increased left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), and increased coronary flow (CF). The hydroxyl radical scavenger thiourea inhibited the H 2O 2-induced effects. Perfusion with three lipoxgenase inhibitors, AA861, BWA4C, and diethylcarbamazine, in adition to H 2O 2, augmented the decrease of LVDP and the increase of LVEDP induced by H 2O 2. The cyclooxygenase inhibitor indomethacin had the same effects. The H 2O 2-induced increased in CF was not influenced by diethylcarbamazine, but inhibited by all other drugs. Control perfusion with drugs alone did not influence cardiac function. In conclusion, inhibition of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase augmented the depression of cardiac function induced by TOM. Leukotrienes and prostanoids appear to be protective against H 2O 2-induced cardiac injury.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
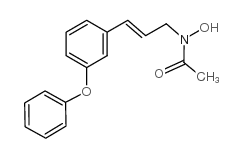 |
BW A4C
CAS:106328-57-8 |
C17H17NO3 |
|
Effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on the growth of murin...
1994-07-01 [Br. J. Cancer 70(1) , 6-10, (1994)] |
|
The 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor BWA4C impairs osteoclastic reso...
1995-08-01 [Bone 17(2) , 185-91, (1995)] |
|
A test system for leukotriene synthesis inhibitors based on ...
1997-10-01 [Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 356(4) , 441-5, (1997)] |
|
Effects of a lipoxygenase inhibitor on digoxin-induced cardi...
1997-11-01 [Gen. Pharmacol. 29(5) , 789-92, (1997)] |
|
Role of lipid hydroperoxides in the activation of 15-lipoxyg...
1996-06-04 [Biochemistry 35(22) , 7197-203, (1996)] |