Perinatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls Aroclor 1016 or 1254 did not alter brain catecholamines nor delayed alternation performance in Long-Evans rats.
E A Zahalka, D H Ellis, E S Goldey, M E Stanton, C Lau
文献索引:Brain Res. Bull. 55(4) , 487-500, (2001)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Several reports have indicated that polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) altered development of biogenic amine systems in the brain, impaired behavioral performances, and disrupted maturation of the thyroid axis. The current study examines whether these developmental effects of PCB are correlated. Timed-pregnant Long-Evans rats were gavaged with the PCB mixture Aroclor 1016 (A-1016, 10 mg/kg) from gestation day (GD) 6 to parturition. Some pups continued to receive daily oral administration of PCB (10 mg/kg) until weaning at postnatal day (PD) 21. Another group of pregnant rats was given Aroclor 1254 (A-1254, 8 mg/kg) daily from GD 6 to weaning. At various age intervals, rats were sacrificed and six brain regions (prefrontal cortex, striatum, hippocampus, diencephalon, cerebellum, midbrain + brain stem) were removed and analyzed for dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE) levels by high-performance liquid chromatography. In addition, transmitter turnover rates were determined after an acute treatment of alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine. Serum samples were collected and analyzed for triiodothyronine (T(3)) and thyroxine (T(4)) by radioimmunoassay. Behaviorally, rats were evaluated for spatial learning and memory by means of T-maze delayed alternation and Morris maze tasks on PD 23 and PD 70, respectively. A-1016 treatment produced only small and transient reductions in body weight gain, and generally did not alter the thyroid status of the developing rats. It did not cause any significant changes in DA or NE level, or turnover rate in any of the brain regions examined, nor did it affect behavioral measures of cognitive development. In contrast, perinatal exposure to A-1254 led to marked deficits of growth, and sharply reduced serum T(4), although T(3) remained largely unaffected. Accompanying this hormonal imbalance, brain NE contents in the A-1254-exposed pups were reduced, although brain DA was not significantly affected; no demonstrable neurobehavioral deficits were seen in the T-maze or Morris maze tests. These results indicated that development of central noradrenergic neurons was compromised by perinatal exposure to A-1254 but not A-1016, and both PCB mixtures failed to alter behavioral performances.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
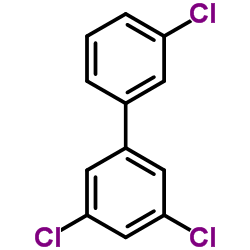 |
亚老哥尔 1016
CAS:12674-11-2 |
C12H7Cl3 |
|
Acute exposure to aroclor 1016 or 1260 differentially affect...
2004-03-14 [Toxicol. Lett. 148(1-2) , 29-40, (2004)] |
|
Selective induction and inhibition of liver and lung cytochr...
1985-05-01 [Toxicology 35(2) , 83-94, (1985)] |
|
The effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclors 1016 and ...
1984-07-01 [Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 13(4) , 493-9, (1984)] |
|
Reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls in sed...
2003-06-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 22(6) , 1214-20, (2003)] |
|
Assessing ongoing sources of dissolved-phase polychlorinated...
2013-03-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 32(3) , 535-40, (2013)] |