| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
雷帕霉素
CAS:53123-88-9 |
|
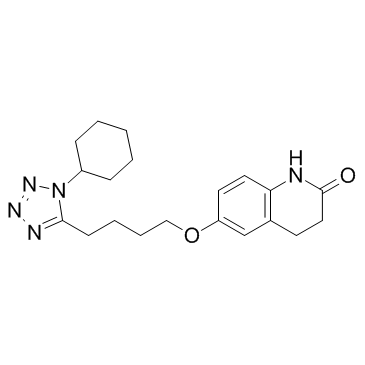 |
西洛他唑
CAS:73963-72-1 |
|
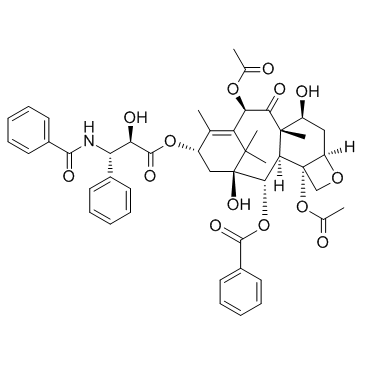 |
紫杉醇
CAS:33069-62-4 |
|
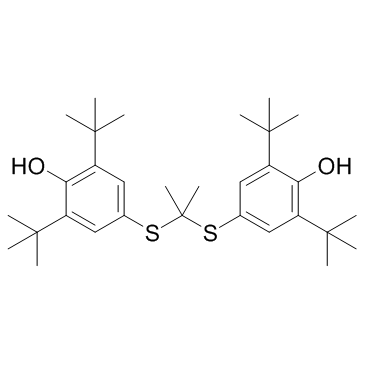 |
丙丁酚
CAS:23288-49-5 |
|
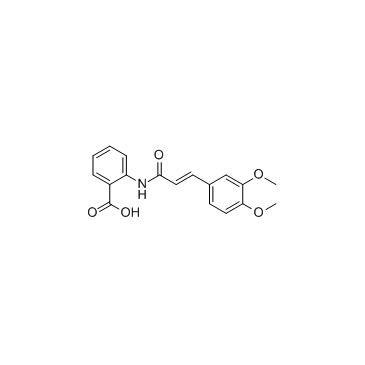 |
曲尼司特
CAS:53902-12-8 |