| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
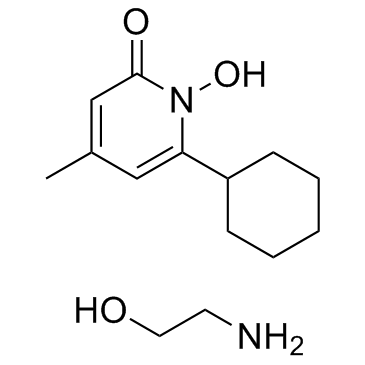 |
环吡酮胺
CAS:41621-49-2 |
|
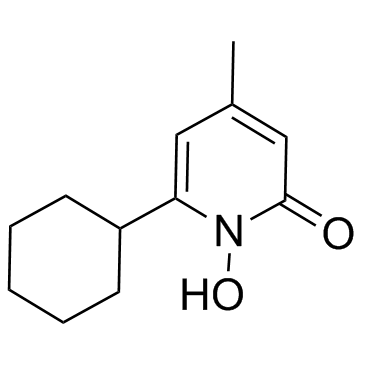 |
环吡酮胺
CAS:29342-05-0 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
环吡酮胺
CAS:41621-49-2 |
|
 |
环吡酮胺
CAS:29342-05-0 |