Molecular basis for the origin of differential spectral and binding profiles of dansylamide with human carbonic anhydrase I and II.
Mustafa M Demir, Bengisu Ozen, Serdar Ozçelik
文献索引:Biochemistry 44(10) , 3673-82, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Sulfonamide derivatives serve as potent inhibitors of carbonic anhydrases (CAs), and a few such inhibitors have been currently used as drugs for the treatment of different pathogenic conditions in humans. In pursuit of designing the isozyme-specific inhibitors of human CAs, we observed that the fluorescence spectral properties and binding profiles of a fluorogenic sulfonamide derivative, 5-(dimethylamino)-1-naphthalenesulfonamide (dansylamide, DNSA), were markedly different between the recombinant forms of human carbonic anhydrase I (hCA I) and II (hCA II). The kinetic evaluation of the overall microscopic pathways for the binding of DNSA to hCA I versus hCA II revealed that the protein isomerization step served as a major determinant of the above discrepancy. Arguments are presented that the detailed structural-functional investigations of enzyme-ligand interactions may provide insights into designing the isozyme-specific inhibitors of CAs.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
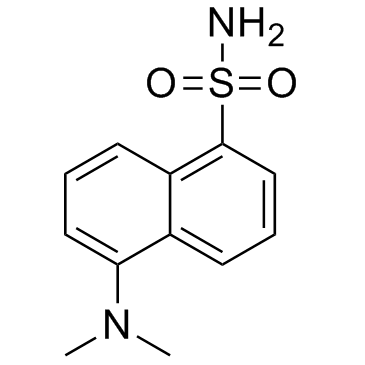 |
丹酰胺
CAS:1431-39-6 |
C12H14N2O2S |
|
Macromolecular Systems with MSA-Capped CdTe and CdTe/ZnS Cor...
2015-11-11 [ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7 , 24778-90, (2015)] |
|
Alteration of human serum albumin tertiary structure induced...
2016-01-15 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 153 , 560-5, (2015)] |
|
Optimizing Multiple Analyte Injections in Surface Plasmon Re...
2015-01-01 [Sci. Rep. 5 , 15855, (2015)] |
|
Nutritional and health-promoting properties of bean paste fo...
2015-11-01 [Food Funct. 6 , 3560-6, (2015)] |
|
How many antimicrobial peptide molecules kill a bacterium? T...
2014-09-19 [ACS Chem. Biol. 9(9) , 2003-7, (2014)] |